文件系统的试验比较简单,第一个实验是扩展文件大小,第二个实验则是实现软链接。
Large File
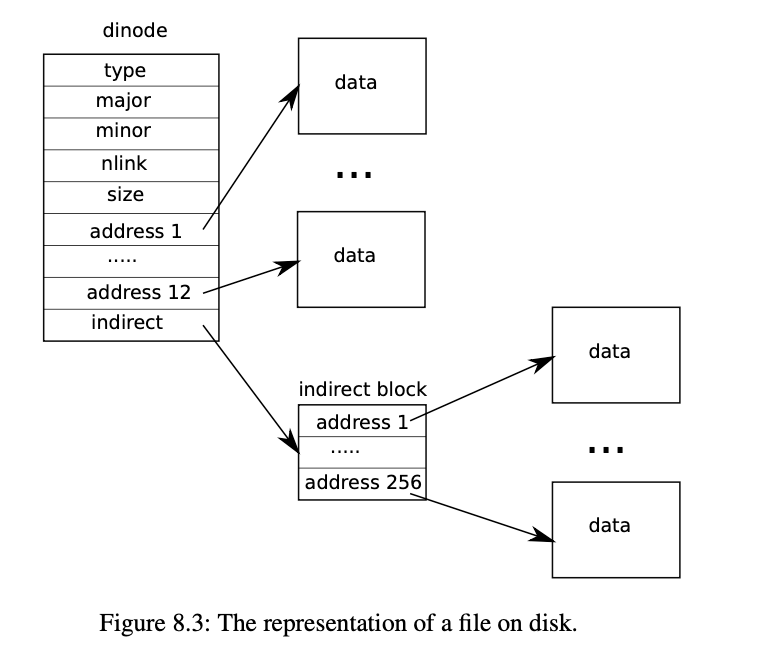
原本的文件只有一级索引块,现在要改造成二级索引块,大小变成 11 + 256 + 256*256.
1
2
3
4
5
| #define NDIRECT 11
#define NINDIRECT (BSIZE / sizeof(uint))
#define NSINDIRECT (BSIZE / sizeof(uint))*(BSIZE / sizeof(uint))
#define MAXFILE (NDIRECT + NINDIRECT + NSINDIRECT)
|
修改宏定义,然后多级读即可
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
| static uint bmap(struct inode *ip, uint bn)
{
uint addr, *a;
struct buf *bp;
if(bn < NDIRECT){
if((addr = ip->addrs[bn]) == 0)
ip->addrs[bn] = addr = balloc(ip->dev);
return addr;
}
bn -= NDIRECT;
if(bn < NINDIRECT){
if((addr = ip->addrs[NDIRECT]) == 0)
ip->addrs[NDIRECT] = addr = balloc(ip->dev);
bp = bread(ip->dev, addr);
a = (uint*)bp->data;
if((addr = a[bn]) == 0){
a[bn] = addr = balloc(ip->dev);
log_write(bp);
}
brelse(bp);
return addr;
}
bn -= NINDIRECT;
if(bn < NSINDIRECT){
int first_index = bn / 256;
int second_index = bn % 256;
if((addr = ip->addrs[1+NDIRECT]) == 0)
ip->addrs[1+NDIRECT] = addr = balloc(ip->dev);
bp = bread(ip->dev, addr);
a = (uint*)bp->data;
if((addr = a[first_index])==0){
a[first_index] = addr = balloc(ip->dev);
log_write(bp);
}
brelse(bp);
bp = bread(ip->dev, addr);
a = (uint*)bp->data;
if((addr = a[second_index])==0){
a[second_index] = addr = balloc(ip->dev);
log_write(bp);
}
brelse(bp);
return addr;
}
panic("bmap: out of range");
}
void itrunc(struct inode *ip)
{
int i, j, k;
struct buf *bp, *cp;
uint *a, *b;
for(i = 0; i < NDIRECT; i++){
if(ip->addrs[i]){
bfree(ip->dev, ip->addrs[i]);
ip->addrs[i] = 0;
}
}
if(ip->addrs[NDIRECT]){
bp = bread(ip->dev, ip->addrs[NDIRECT]);
a = (uint*)bp->data;
for(j = 0; j < NINDIRECT; j++){
if(a[j])
bfree(ip->dev, a[j]);
}
brelse(bp);
bfree(ip->dev, ip->addrs[NDIRECT]);
ip->addrs[NDIRECT] = 0;
}
if(ip->addrs[1+NDIRECT]){
bp = bread(ip->dev, ip->addrs[1+NDIRECT]);
a = (uint*)bp->data;
for(j=0; j< 256; ++j){
cp = bread(ip->dev, a[j]);
b = (uint*)cp->data;
for(k=0; k<256; ++k){
if(b[k]) bfree(ip->dev, b[k]);
}
brelse(cp);
bfree(ip->dev,a[j]);
a[j] = 0;
}
brelse(bp);
bfree(ip->dev, ip->addrs[1+NDIRECT]);
ip->addrs[NDIRECT] = 0;
}
ip->size = 0;
iupdate(ip);
}
|
Symbolic links
区别软链接与硬链接:
- 软链接:它是一个t特殊的文件,文件的内容是一个路径,这个路径指向被链接的文件
- 硬链接:它是一个目录项,这个目录项指向了目标文件
1
2
3
4
| struct dirent {
ushort inum;
char name[DIRSIZ];
};
|
name是目录项的名字,inum则是它指向的inode块号,那么就是通过inum指向目标文件。
open调用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| uint64 sys_open(void) {
...
if (omode & O_CREATE) {
ip = create(path, T_FILE, 0, 0);
if (ip == 0) {
end_op();
return -1;
}
} else {
if ((ip = namei(path)) == 0) {
end_op();
return -1;
}
ilock(ip);
if (ip->type == T_DIR && omode != O_RDONLY) {
iunlockput(ip);
end_op();
return -1;
}
int count = 0;
while (ip->type == T_SYMLINK && omode != O_NOFOLLOW) {
if(count > 10 ){
iunlockput(ip);
end_op();
return -1;
}
if (readi(ip, 0, (uint64)path, 0, MAXPATH)==-1) {
iunlockput(ip);
end_op();
return -1;
}
iunlockput(ip);
if ((ip = namei(path)) == 0) {
end_op();
return -1;
}
ilock(ip);
count++;
}
...
}
|
对于软链接还需要recursively查找,限制递归深度来模拟递归。
symbolic调用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| uint64 sys_symlink(void) {
char target[MAXPATH], path[MAXPATH];
if (argstr(0, target, MAXPATH) < 0 || argstr(1, path, MAXPATH) < 0)
return -1;
struct inode* ip;
begin_op();
if((ip=create(path, T_SYMLINK, 0, 0)) == 0){
end_op();
return -1;
}
if(writei(ip, 0, (uint64)target, 0, strlen(target)) == -1){
iunlockput(ip);
end_op();
return -1;
}
iunlockput(ip);
end_op();
return 0;
}
|
实现symblic,先创建inode,然后再将链接路径名写进去。
